Integration of Electric Vehicles into the Global Energy System
Electric vehicles (EVs) have emerged as transformative forces that not only reshape transportation but also redefine global energy systems. By 2025, the rapid growth of EV adoption worldwide is altering the balance between energy production, distribution, and consumption. Thus, EV integration into global energy systems has evolved into a multidimensional issue encompassing technological, economic, political, and environmental dimensions.
Impact on Energy Demand and Grids
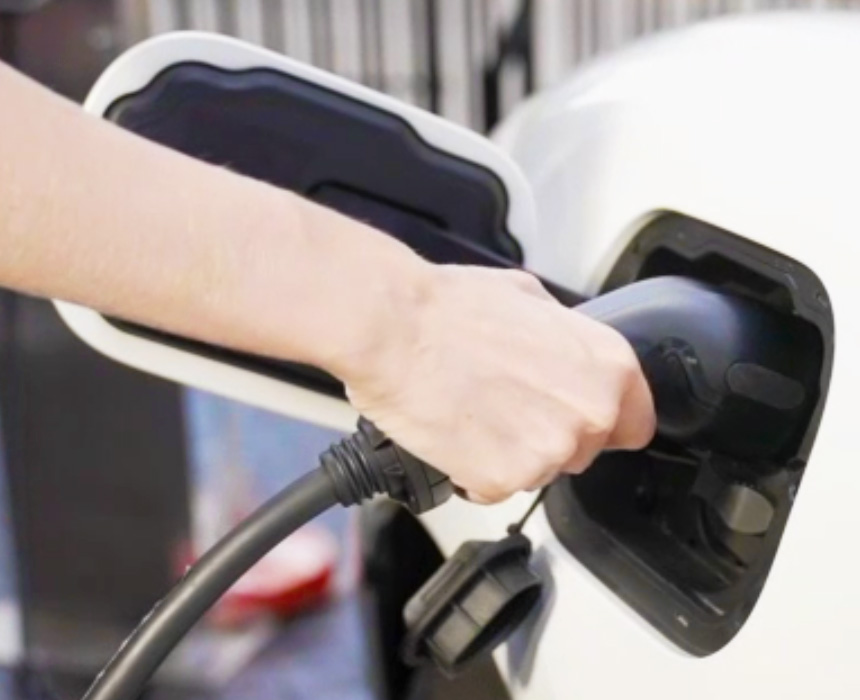
The widespread use of EVs significantly increases global energy demand. In densely populated regions, the proliferation of fast-charging stations places new burdens on distribution grids. This necessitates strengthening traditional infrastructure, adopting smart grid technologies, and implementing demand-response mechanisms. Without these measures, the surge in EV-related demand could threaten energy security and grid stability worldwide.
Alignment with Renewable Energy
One of the most critical aspects of EV integration lies in its synergy with renewable energy. Variable sources such as solar and wind can be better utilized through the storage potential of EV batteries. Particularly, vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technologies enable EVs to act as decentralized storage units, feeding excess renewable generation back into the system. As a result, EVs become both consumers and suppliers of energy, strengthening resilience and accelerating decarbonization.
Economic and Policy Dimensions
EV integration is not only a technical challenge but also a strategic transformation of the global energy economy. Reduced dependence on fossil fuels shifts energy import balances, while new business models (subscription-based charging, digital payments) reshape market structures. International organizations and governments play vital roles by setting standards, creating incentives, and aligning EV integration with global carbon reduction goals.
Socio-Environmental Impacts
From a sustainability perspective, EV integration offers clear benefits: reduced carbon emissions, improved urban air quality, and lower noise pollution. However, issues such as battery production, raw material extraction, and recycling present challenges that could offset some environmental gains if not addressed responsibly on a global scale.
Conclusion
Integrating EVs into the global energy system is a complex, multi-layered process at the intersection of technology, policy, economics, and sustainability. Successful integration will ensure not only the transformation of mobility but also a fundamental reconfiguration of the global energy landscape.