The Strategic Role of Electric Vehicles in a Sustainable Transportation Ecosystem
The global adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) represents far more than just a change in transportation preferences; it is one of the central elements of an economic, environmental, and social transformation. The sustainable transportation ecosystem encompasses reducing carbon emissions, ensuring energy security, transforming cities into smart environments, and shifting user behaviors. EVs stand at the core of this system, forming the backbone of the mobility vision of the future.
Environmental Impact of EVs
Unlike internal combustion engine vehicles, EVs contribute significantly to reducing air pollution due to their zero direct emissions. Yet, this impact must be assessed holistically. The production of batteries, the diversity of energy sources, and the development of recycling mechanisms all play crucial roles in shaping their overall environmental footprint.
The mining of minerals for battery production can harm ecosystems. Therefore, for EVs to achieve true sustainability, circular economy practices and advanced recycling technologies must be prioritized.
Energy Security and Independence
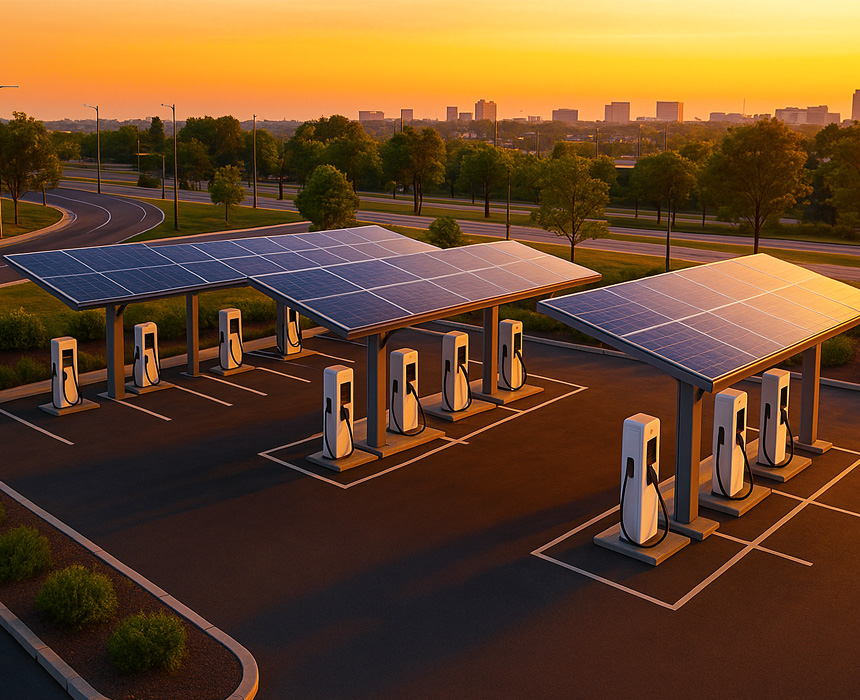
The expansion of EV adoption also directly influences energy policies. By reducing dependency on fossil fuels, countries can strengthen their energy security and minimize geopolitical risks. Integrating renewable energy sources with charging infrastructure is vital, not only for reducing carbon emissions but also for safeguarding energy supply.
Urban Planning and Smart Mobility
The widespread use of EVs demands the redesign of urban infrastructure. Strategic placement of charging stations, intelligent traffic management, integration with public transportation, and the incorporation of micromobility solutions (such as e-bikes and scooters) will define the foundations of future cities.
User Behavior and Social Transformation
EV adoption is driven not only by technological progress but also by shifts in user awareness and perception. Increasing environmental consciousness, cost advantages, and ease of use all play critical roles in consumer decisions.
The ability for users to monitor their carbon footprint, access transparent pricing models, and choose green energy sources accelerates broader social transformation.
Economic Contributions and New Business Models
The EV ecosystem generates not only environmental benefits but also significant economic opportunities. Battery production, software development, charging infrastructure management, and data analytics open new avenues for employment.
In addition, EV-sharing services and subscription-based models create alternative approaches to vehicle ownership and reshape the mobility economy.
Regulations and Standards
The role of EVs in building a sustainable ecosystem is reinforced by national and international regulatory frameworks. In Türkiye, EPDK and TSE; in Europe, UNECE; in the U.S., DOE, FERC, NIST; in Central Asia, O’zbekenergo and O’zDSt; and in Russia, Минэнерго and ГОСТ all provide standards to guide this transformation.
Looking Ahead
In the coming years, EVs will become even more central to sustainable mobility. The commercialization of solid-state batteries, proliferation of ultra-fast charging technologies, deployment of AI-driven mobility solutions, and integration with smart city infrastructures will reinforce the strategic role of EVs in the transportation ecosystem.
Conclusion
EVs are among the key actors of the sustainable transportation ecosystem. From environmental protection and energy security to urban planning and social transformation, their impact is profound. This 6000+ character analysis demonstrates that EVs are not simply a transportation choice but a cornerstone of the future mobility vision.