Next-Generation Battery Technologies and the Future of EVs
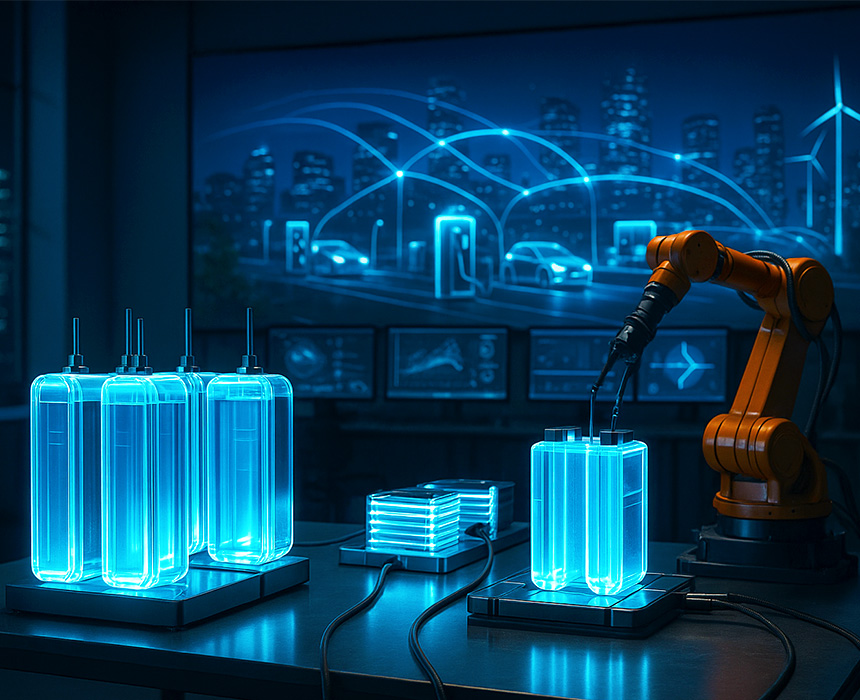
The future of electric vehicles (EVs) is inextricably linked to the rapid advancement of battery technologies. Over the past decade, breakthroughs in chemistry, energy density, and manufacturing have redefined what EVs can achieve. These changes are not limited to range extension or charging speed; they also reshape entire energy systems, transportation planning, and sustainability strategies. Batteries have thus become more than storage units: they are the foundation of tomorrow’s mobility and energy infrastructures.
Currently, lithium-ion batteries dominate the market. They enabled the first mass adoption of EVs, but their limitations in density, safety, cost, and recycling demand new solutions. Solid-state batteries, which replace liquid electrolytes with solid ones, promise to double energy density while improving safety. This innovation could make five-to-ten-minute charging possible without overheating risks. If commercialized at scale, it will mark a fundamental shift similar to the invention of the internal combustion engine.
In parallel, research has turned to sodium-ion and magnesium-ion cells as alternatives to lithium-based chemistries. These elements are far more abundant and geographically diversified, reducing supply-chain vulnerabilities and lowering costs. Chinese companies are piloting sodium-ion batteries for small EVs, while European laboratories are testing magnesium-ion prototypes for long-haul applications.
Equally vital are Battery Management Systems (BMS). These systems oversee charging cycles, voltage, and temperature to prolong battery life. Recent advances integrate AI to predict user habits and adjust charging dynamically. For example, a commuter driving short distances may receive software recommendations that limit charging to 80%, thereby extending battery health. Once their automotive life ends, BMS software can enable “second life” applications, converting batteries into grid storage for renewable energy.
Manufacturing techniques are undergoing a green transformation. Dry electrode processes reduce energy usage by up to 50% compared to traditional methods. Automated robotic assembly lines increase safety and precision while cutting production costs. This makes localized gigafactories more feasible, giving regions independence from Asian supply dominance.
Thermal management is another frontier. Ultra-fast charging requires advanced cooling solutions. Liquid- and immersion-cooling systems allow batteries to withstand extremely high currents without degradation. This is essential for fleet electrification in logistics, public transit, and heavy-duty vehicles.
Digitalization has transformed batteries into dynamic grid assets. Through Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G), EVs can store excess renewable energy during the day and feed it back into the grid at night. In energy-scarce regions, this creates virtual power plants distributed across millions of cars, providing resilience against blackouts.
Altogether, these advancements show that batteries are central to both mobility and energy futures. Solid-state breakthroughs, material diversification, AI-driven management, and sustainable manufacturing converge to make EVs more affordable, reliable, and sustainable than ever before.