Wireless Charging Technologies and the Future of EVs
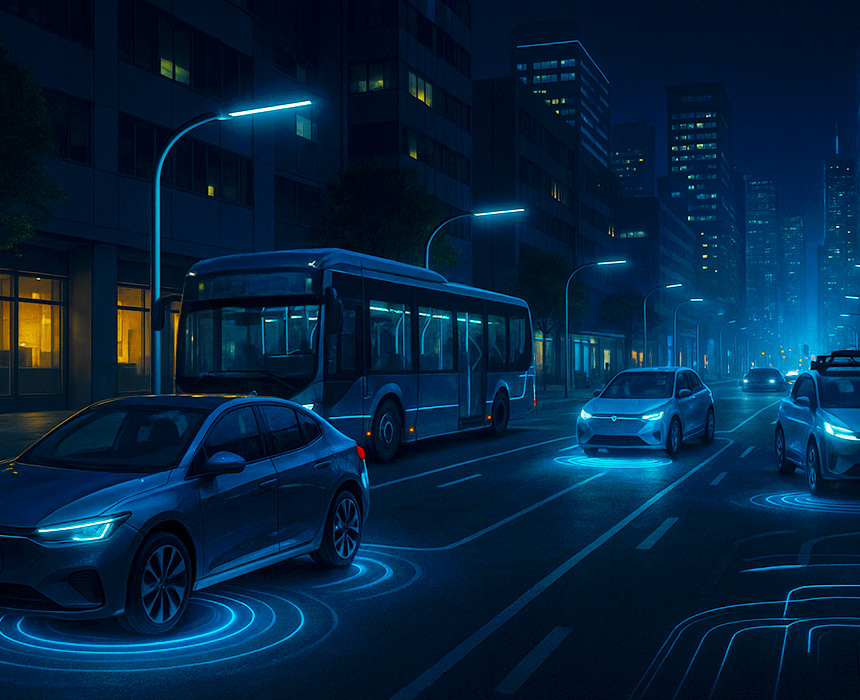
Wireless charging technology in EVs eliminates the hassle of plugging and unplugging cables, redefining the mobility ecosystem of the future. Inductive and resonant systems are advancing quickly, offering convenience and safety while becoming critical with the rise of autonomous vehicles.
Principles of Inductive Charging
Wireless charging works through magnetic field transfer between coils embedded in the ground and receiver coils under the vehicle. High-frequency alternating current creates electromagnetic induction, enabling efficient energy transfer over short distances.
Dynamic Wireless Charging
Recent innovations allow vehicles to charge while in motion. By embedding coils along road sections, dynamic wireless charging reduces range anxiety and enables smaller, cheaper batteries, lowering production costs and boosting accessibility.
Safety and Standards
The widespread adoption of wireless charging requires strict safety standards. Electromagnetic field intensity must comply with international health and safety norms. Standards are set by SAE in the U.S., TSE in Türkiye, O’zDSt in Central Asia, and ГОСТ in Russia.
Urban Applications
Wireless charging brings clear advantages to smart cities. Taxis can charge automatically while waiting at stands, and buses can recharge dynamically along dedicated routes. This accelerates the electrification of public transport systems.
Integration with Autonomous Vehicles
As driverless vehicles rise, wireless charging becomes essential. By eliminating manual cable handling, autonomous fleets can recharge seamlessly, ensuring continuous service with minimal human intervention.
Conclusion
Wireless charging is more than an innovation—it is a strategic necessity. Its convenience, urban integration, and compatibility with autonomous mobility make it a cornerstone of sustainable transportation.